Description
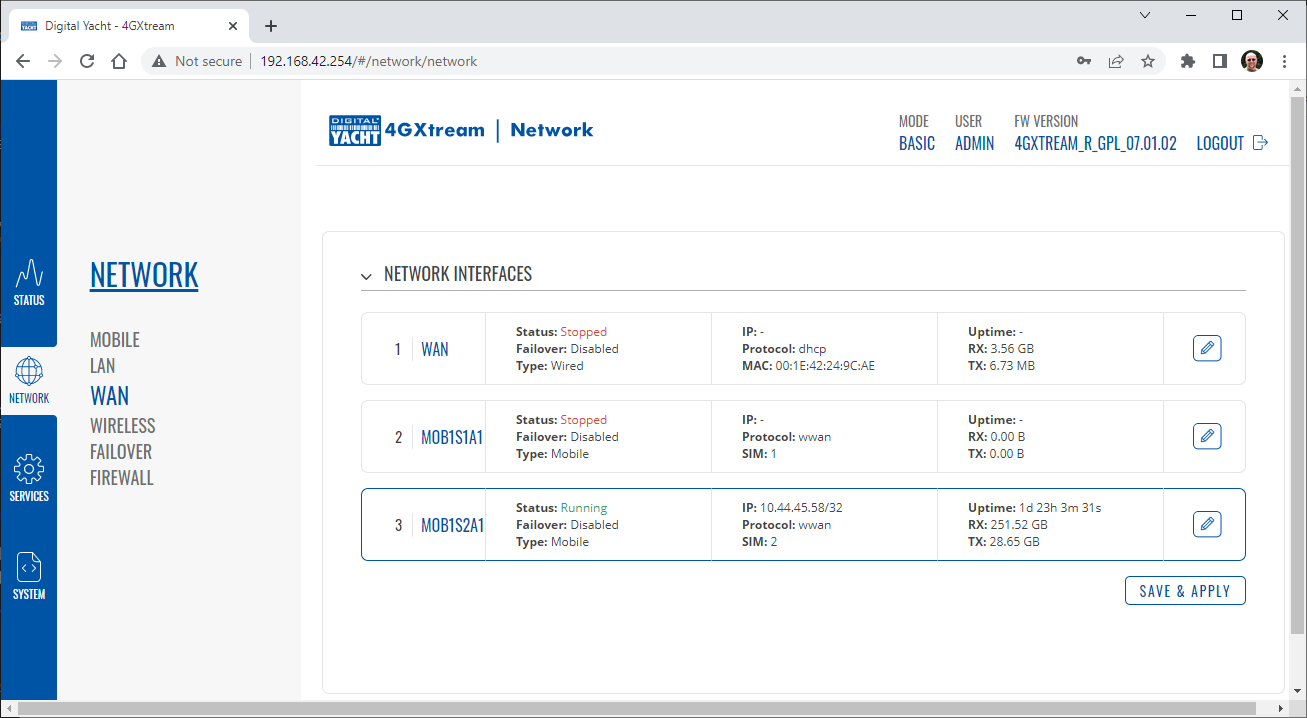
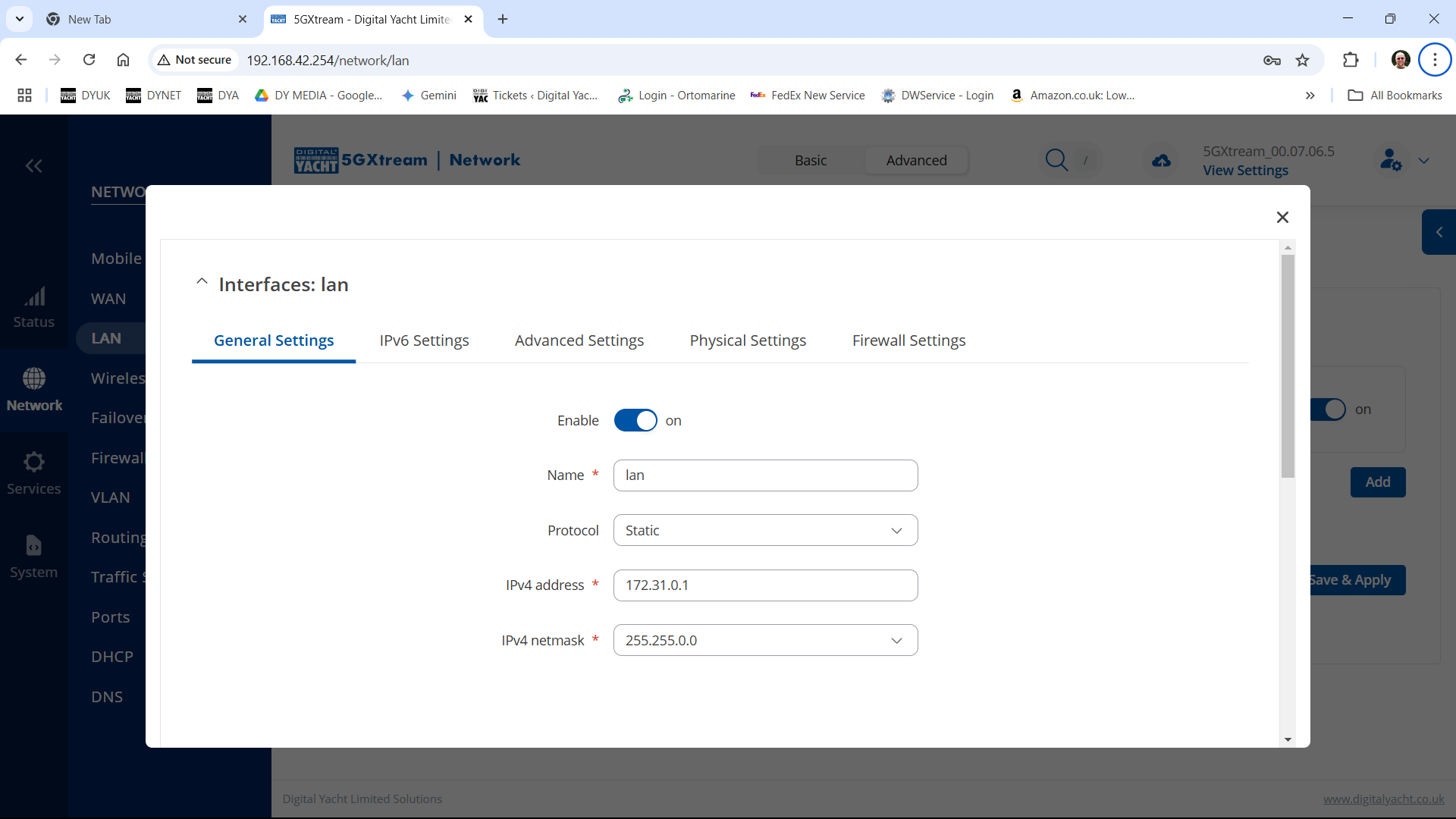
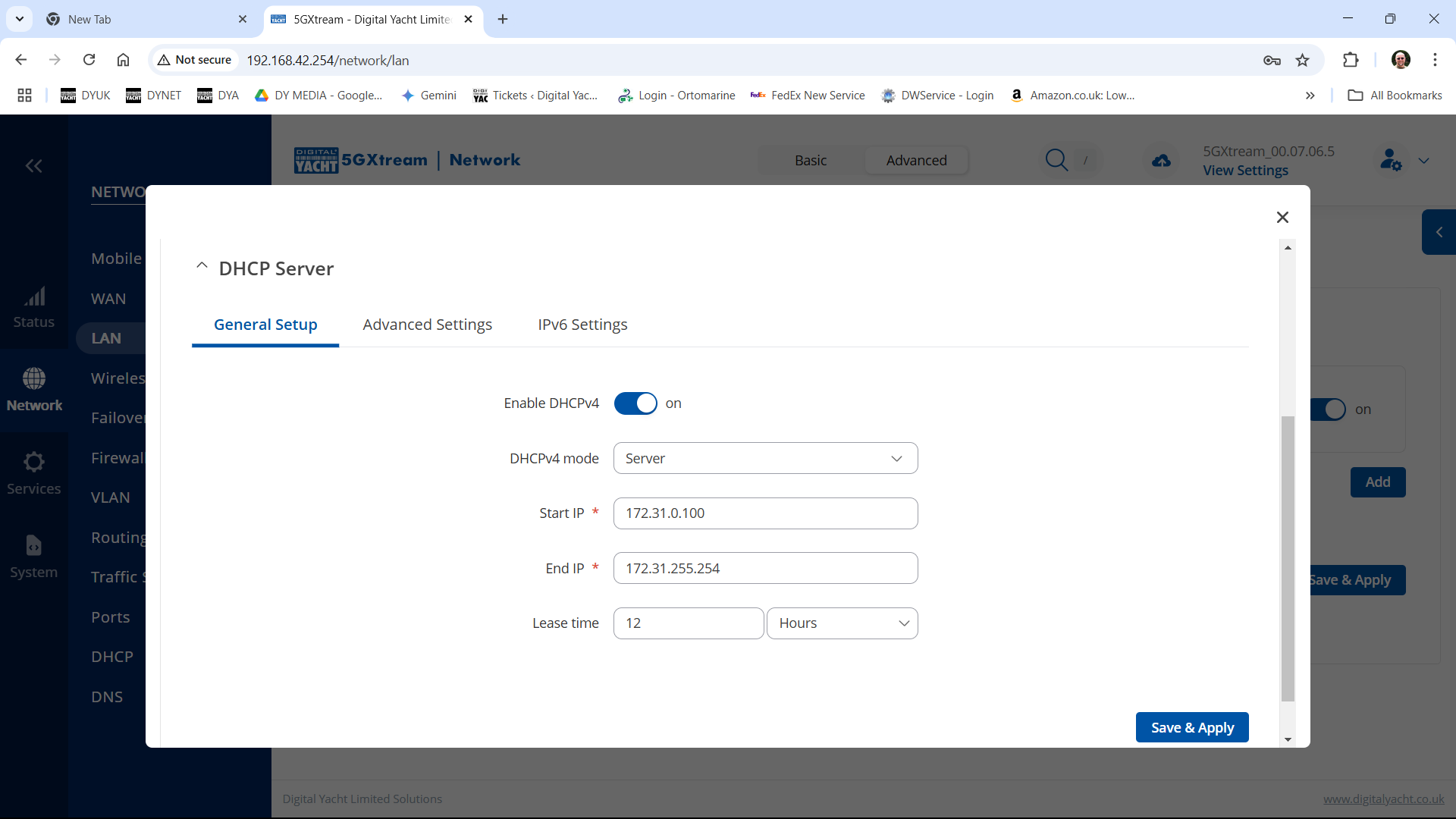
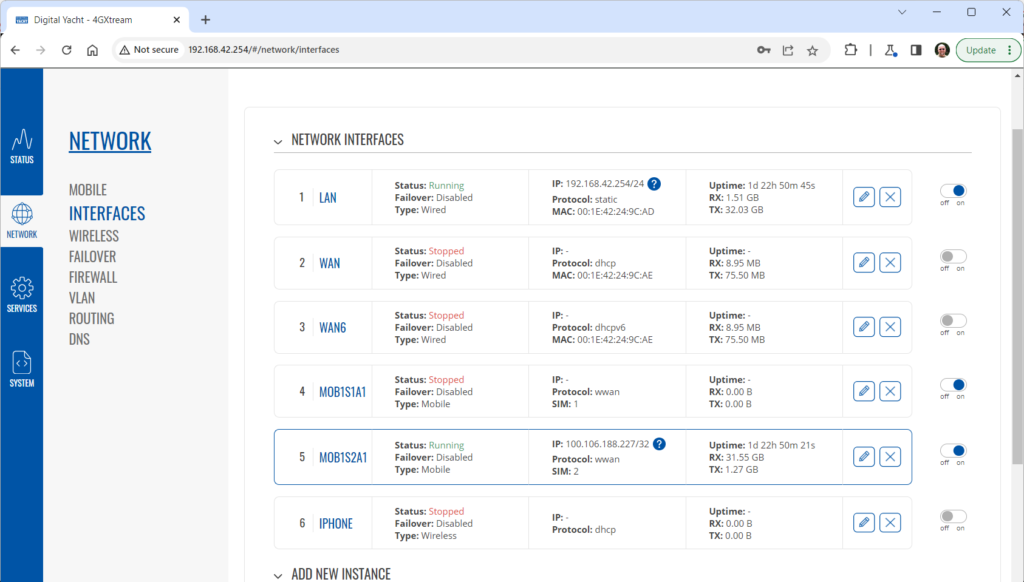
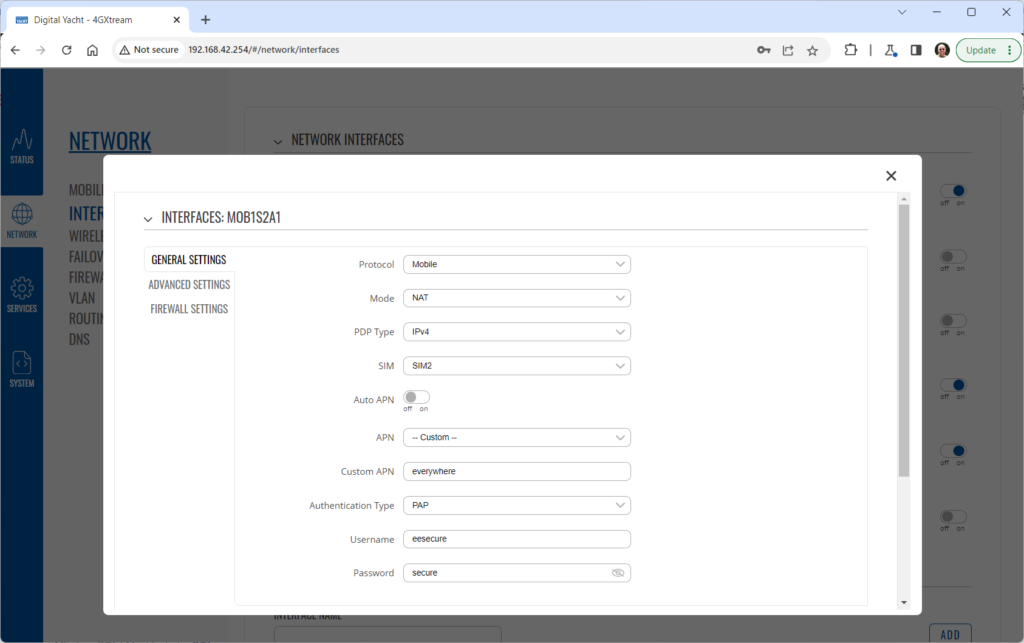
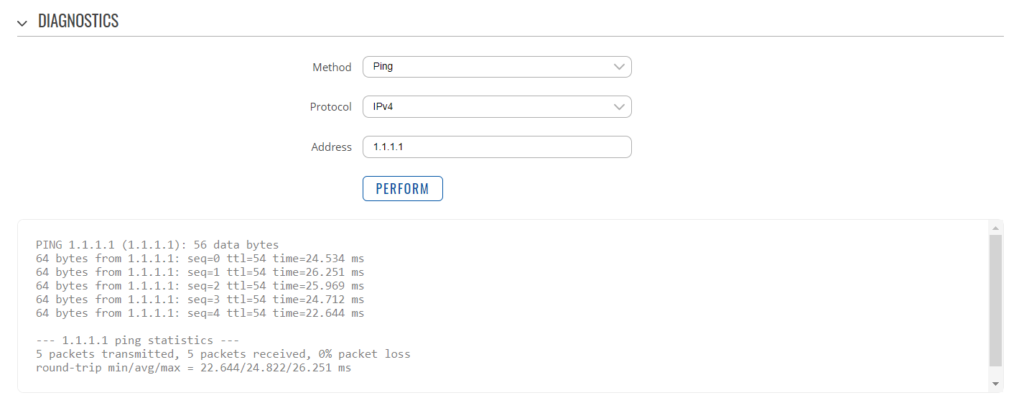
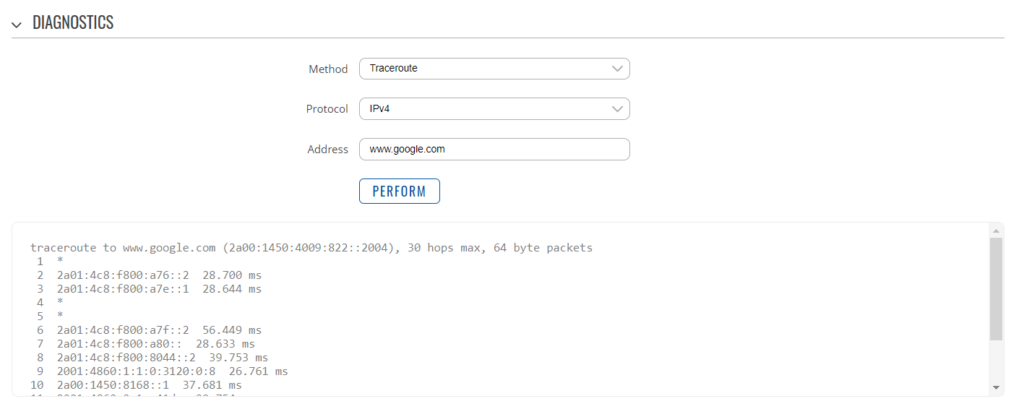
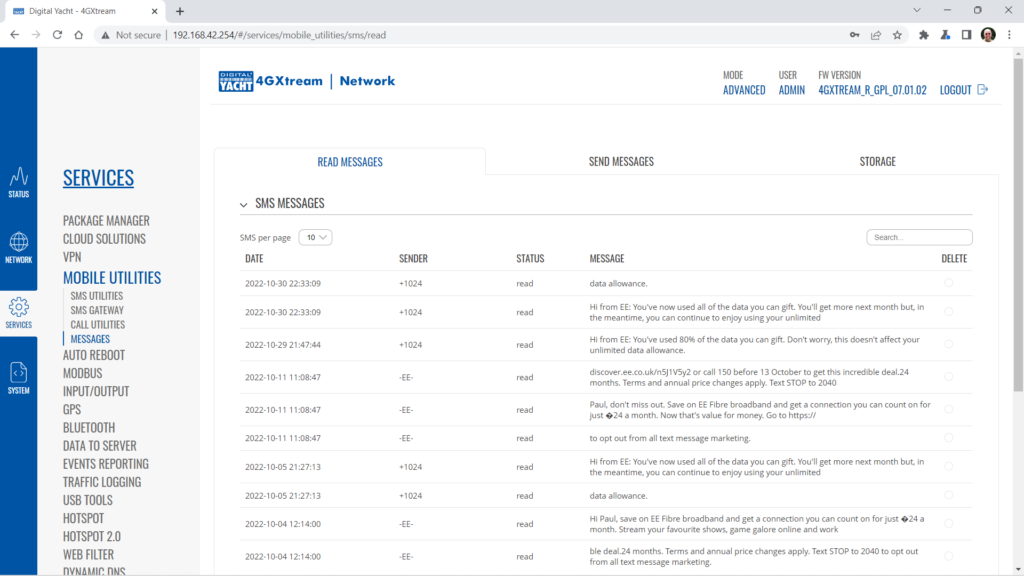
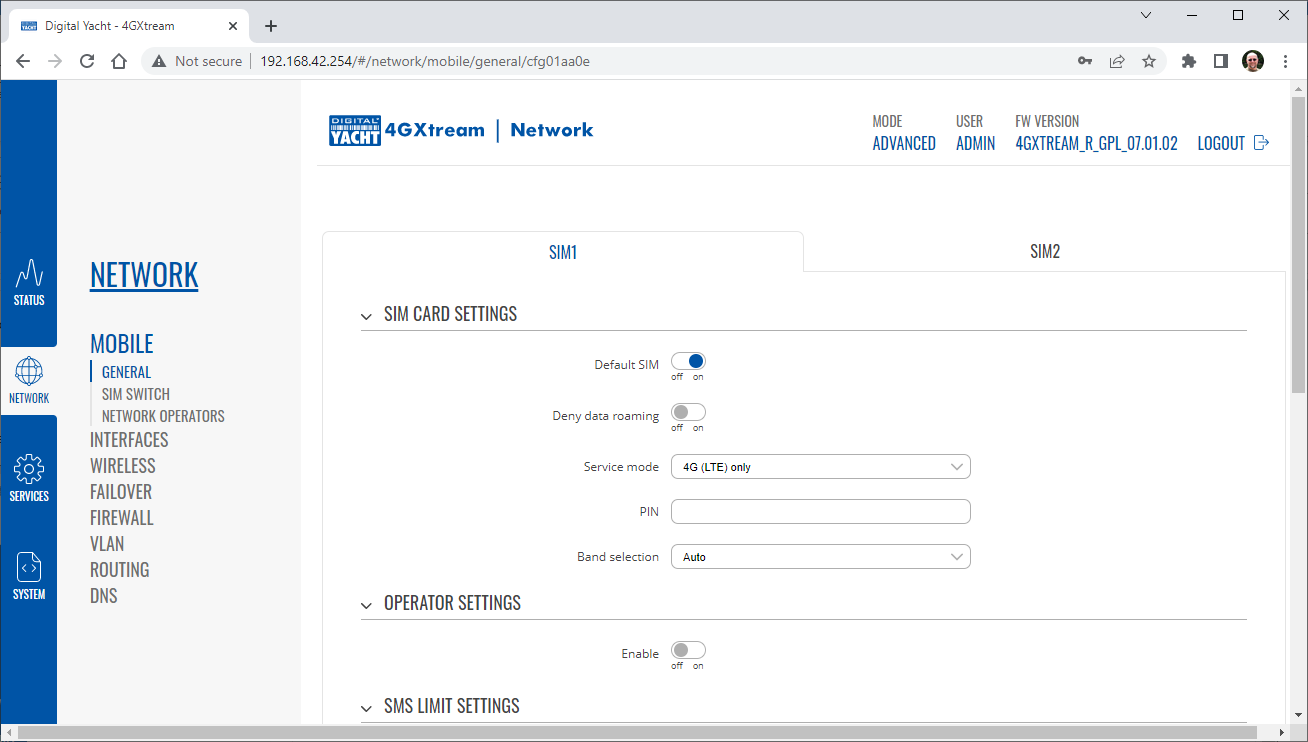
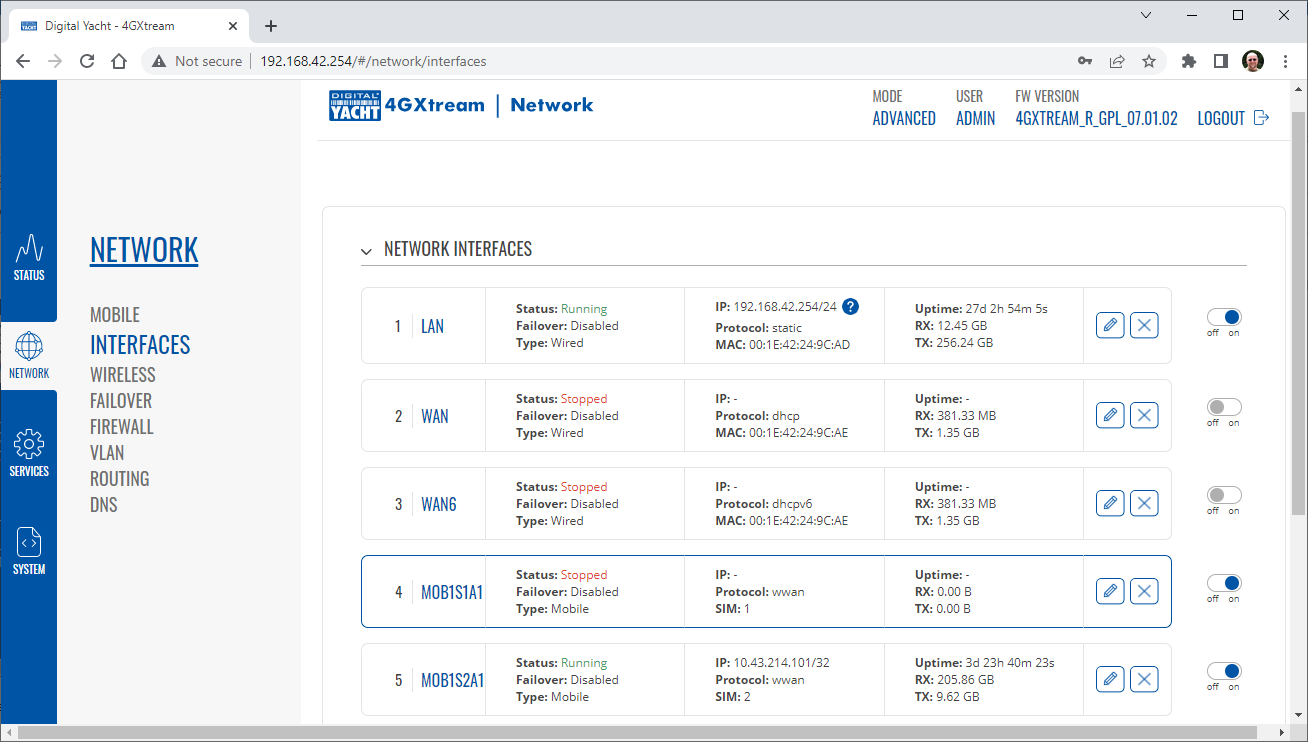
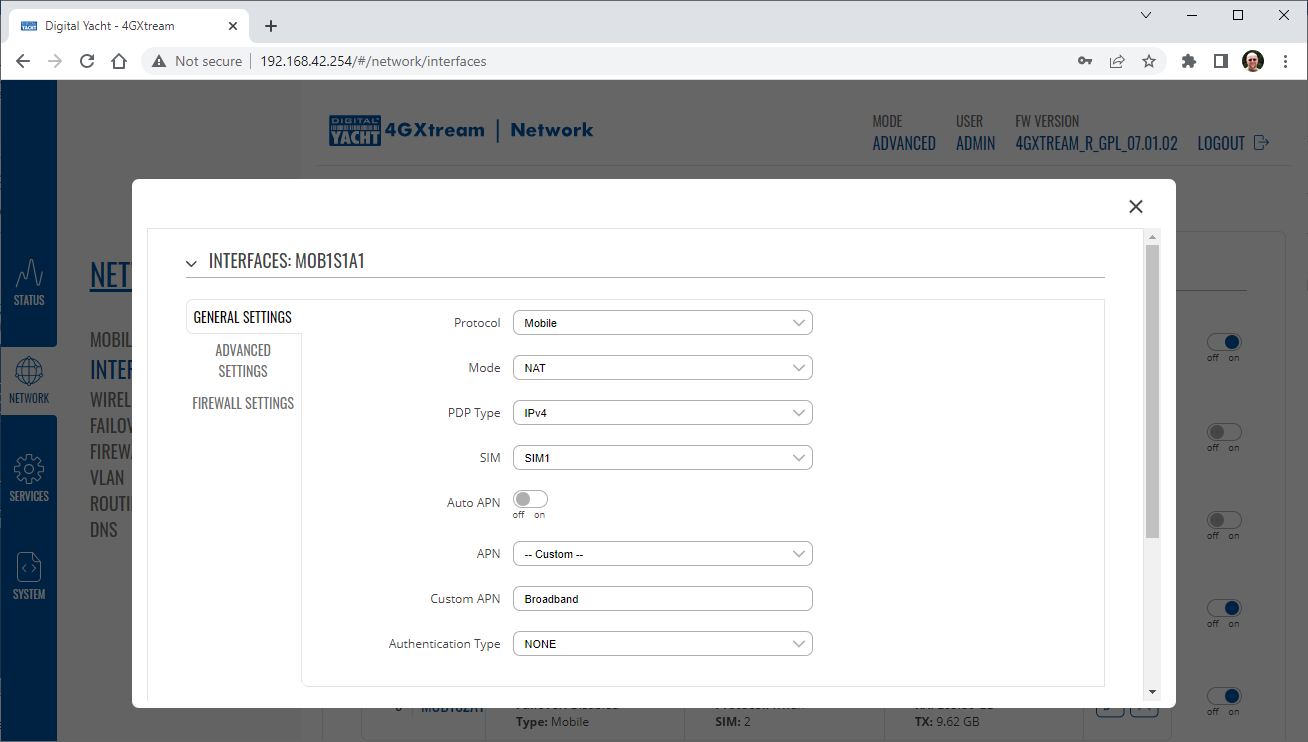
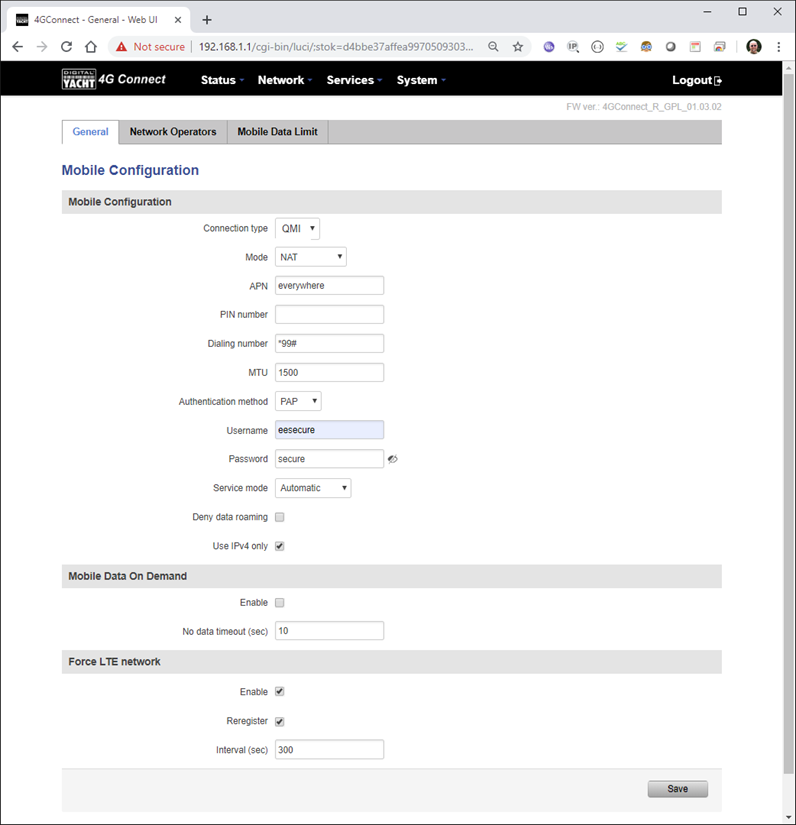
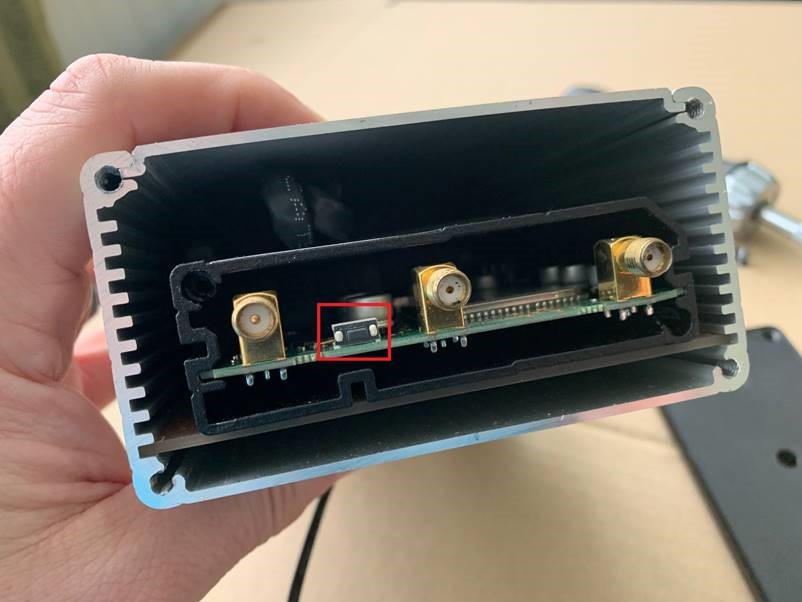
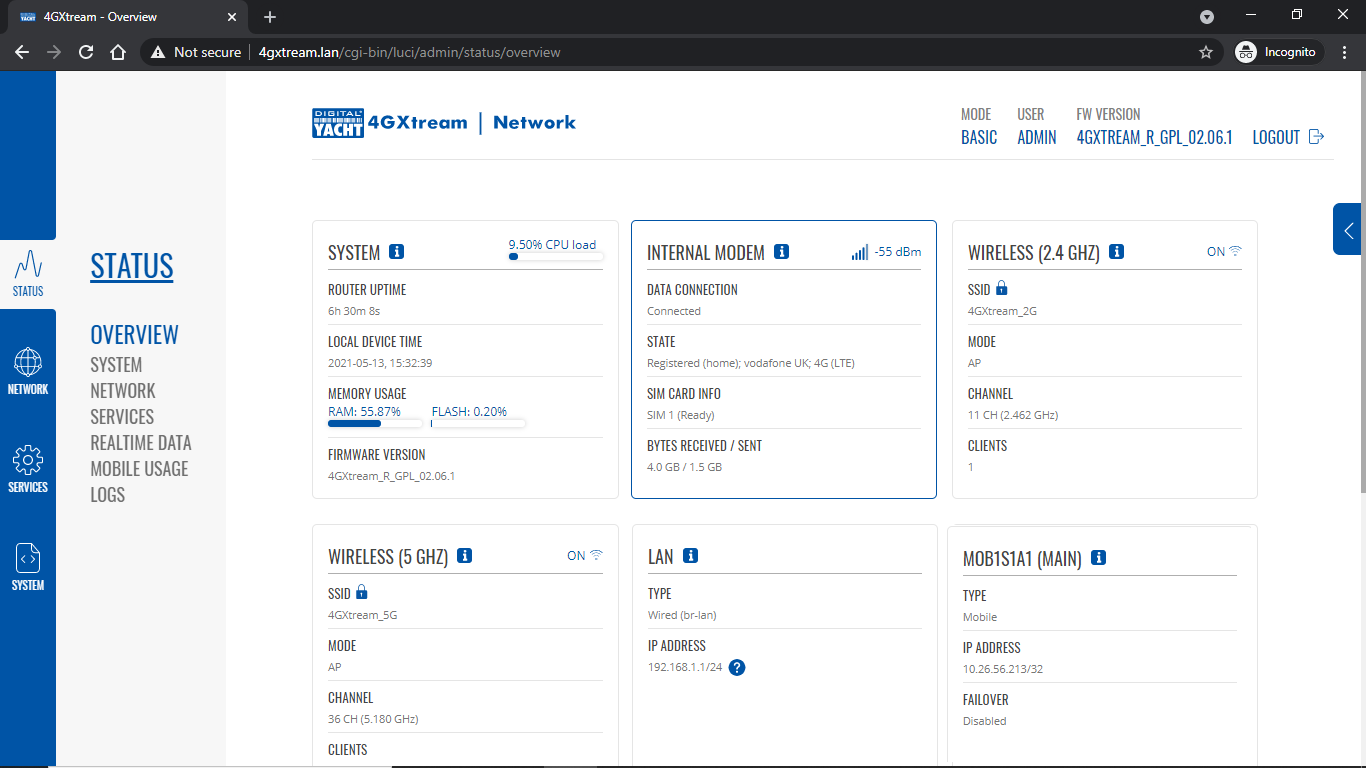
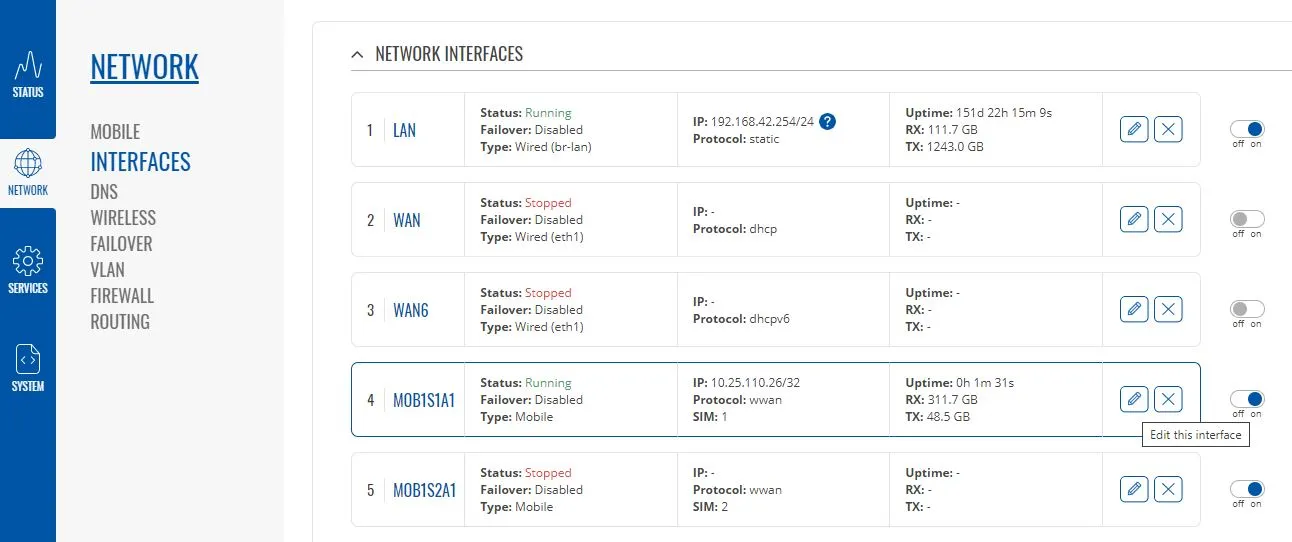
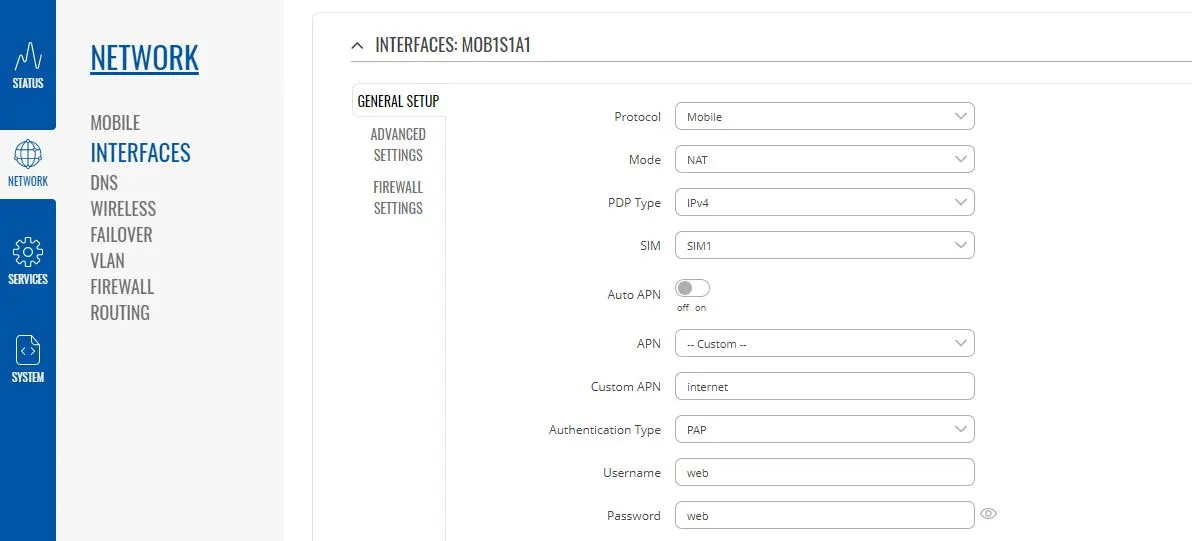
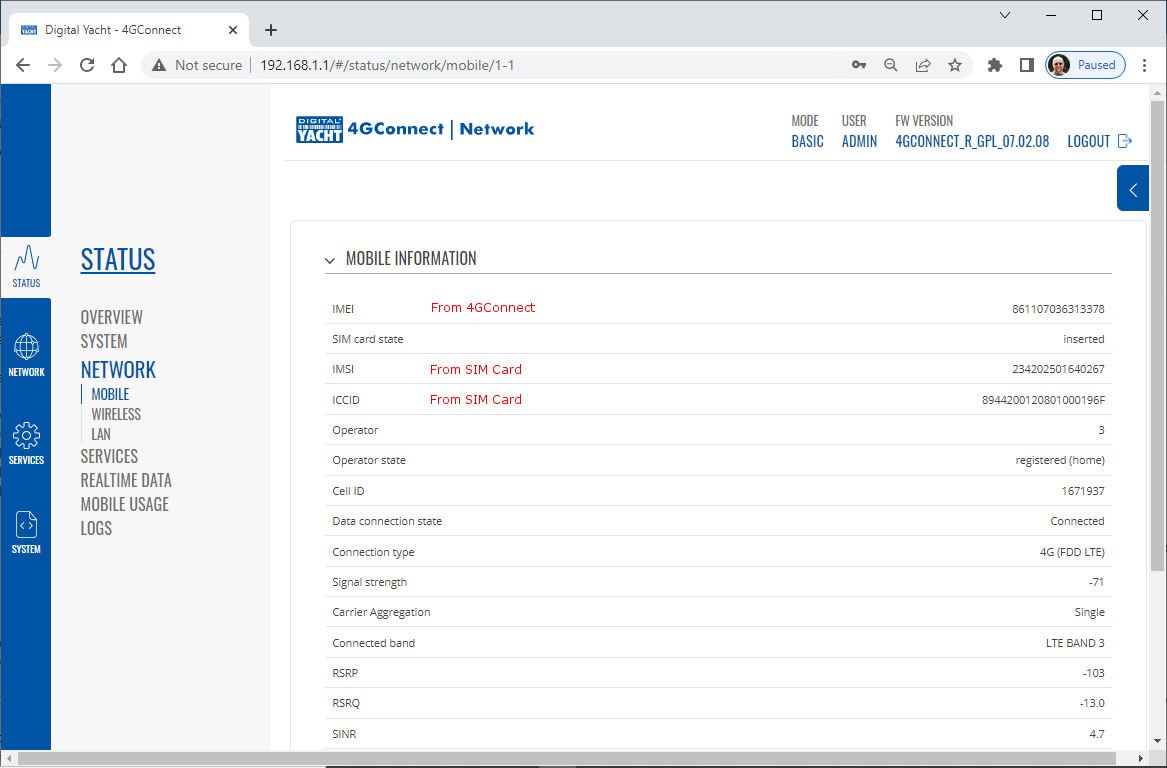
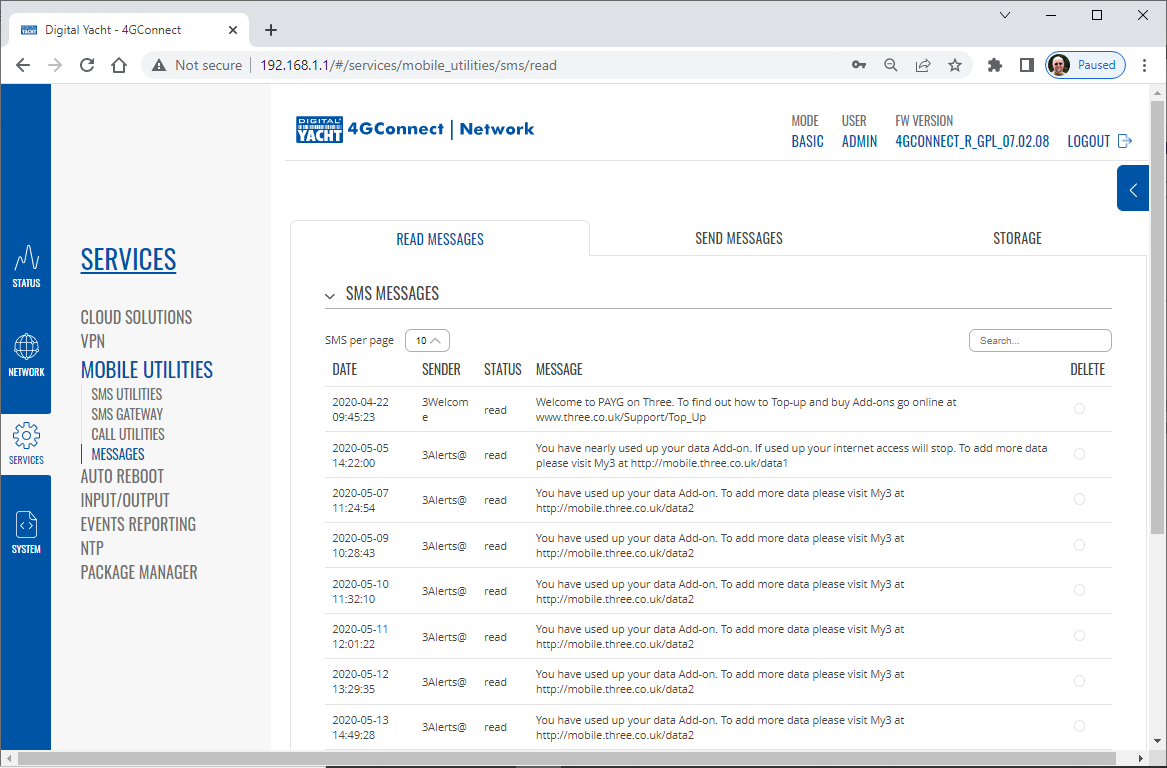
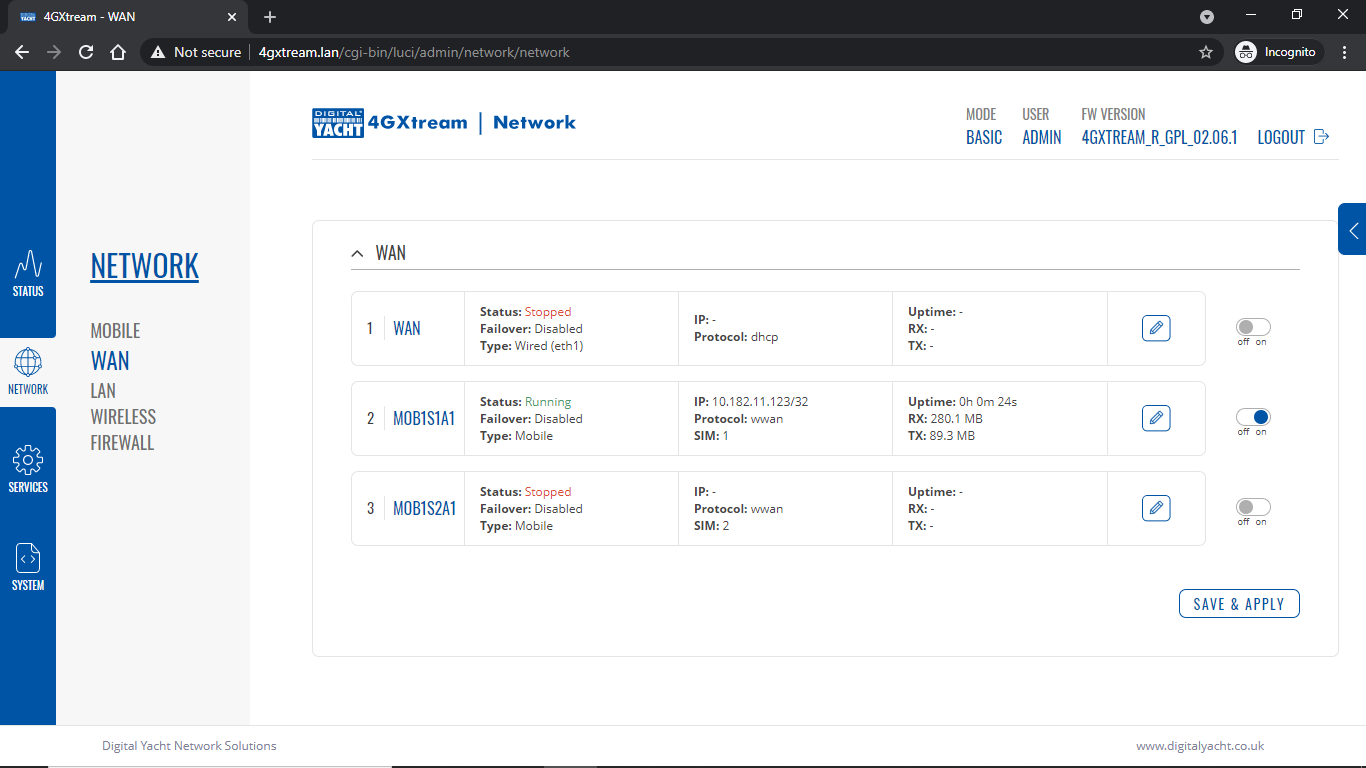
To change the IP address range used on the LAN network, go to NETWORK>LAN and then click the EDIT option. Set as shown below and click SAVE&APPLY. When the unit reboots, reconnect and access the web interface at the address you have set. In the example below, we have set the addres: 172.31.0.1 so when we reboot the unit, to access the web interface in our example, we need to write the address http://172.31.0.1 The DHCP range is set automatically, but if they want to check or change this, go back to NETWORK>LAN and click EDIT and the DHCP settings are in the Firewall Settings tab. If you have a very low internet speed (less than 5m/sec) then several factors can interfere with your internet speed. When a device is connected to one of our wireless 4G routers, the router has to “route” the data, which takes time. The typical 2.4GHz speed of 50Mbps is shared across all devices on the wireless network: more devices, less speed It is not uncommon for other 2.4GHz wireless networks to be present on a modern boat; MFD, Charger/Inverter, AIS, etc. Each network, will potentially cause interference and slower speeds To get a better speed, the best solution is to connect your laptop via Ethernet. With the 4G Connect Pro, you can get internet up to 60m/s via Ethernet but via WiFi, a good connection would be 25-35Mbps. Although the approach you are taking with DDNS and Port Forwarding would work well on a conventional land based network, that is connected to the internet via a Cable/ADSL router, there are several reasons why they may not work on a mobile network: It’s worth noting that some mobile network providers may offer specific plans or services that allow for more open network access or even static IP addresses, which can facilitate DDNS and port forwarding. However, these options may come with additional costs and may not be available on all networks or in all regions. Overall, the combination of NAT, carrier restrictions, firewall policies, and dynamic IP addresses on mobile networks can make it challenging for DDNS and port forwarding to function reliably. If you require remote access to devices on a mobile network, you may need to explore alternative solutions such as VPN (Virtual Private Network) or cloud-based services that facilitate remote access without relying on DDNS or port forwarding. Our 4G products (4GConnect and 4GXtream) provide good internet connectivity over 4G mobile networks and we know that they are used by some of our customers to remotely access their marine systems. To remotely access the systems on a boat, the normal method is for the equipment on the boat to initiate a secure connection to a cloud server and then you use an App on your mobile device to also access the cloud server. The cloud server then routes you through to your boat’s data, which you can view in almost realtime. This method relies on the equipment manufacturer creating the cloud system and app to make this happen. The best example of this type of system is the Victron VRM system. The second method is to use a VPN service to create a more generic cloud connection, not specific to one manufacturer, which basically connects your mobile device to the boat’s Ethernet network. Once the VPN connection is established, you can remotely do anything that you would normally do when on the boat. Setting up a VPN on our 4G Products is possible, but requires networking knowledge and is not something that Digital Yacht is able to provide support on. You would need to find a suitably experienced IT networking engineer. If you want to explore the VPN solution, I would recommend ZeroTier which can be installed on our 4GXtream and is a free and relatively easy to setup VPN service, that I played with a few years back. OpenVPN is also supported on our 4GXtream. Since the end of 2022, we have started receiving support requests from new EE customers that cannot get their Digital Yacht 4G Products to work with their EE SIM. It would appear that recent EE SIMs have a Virgin Mobile profile included, which is seen as the default APN settings when our products are set to Auto APN mode (default). If your SIM is being correctly read, you are getting a good mobile signal strength, the STATE is shown as “Registered (home); EE; 4G (LTE)” but the DATA CONNECTION is shown as Disconnected, then please try the following settings. Open a browser, go to http://192.168.1.1 and login to the web interface. Now change to ADVANCED mode by clicking on the word BASIC in the top right corner of the web interface. On the menu select NETWORK>INTERFACES and you will see the page below…. Click on the “Pencil” Edit icon for the SIM slot the EE SIM is inserted in – MOB1S2A1 in the example above. Now you need to set Auto APN to OFF and enter the following details in the boxes that appear. Also make sure that PDP Type is set to IPv4 Only and not IPv4/IPv6 which is the default… Once all of the settings are correctly entered, scroll to the bottom of the page and click the “SAVE & APPLY” button. Give the unit 20-30 seconds to apply the settings and reboot the modem and then you should see the DATA CONNECTION change to Connected and you will be online. Many products from leading marine electronics manufacturers now feature a wired and/or wireless network interface. In some larger systems such as those from Navico/Garmin/Raymarine/Furuno, the MFDs, radar scanners, cameras and sonar systems will all be networked together via Ethernet cables. When one of our 4G Products is used as the central wireless router for internet connectivity, some customers have been confused as to whether they can join all of the devices together on one common network. In general, unless indicated differently by the MFD manufacturer, it is best to leave the manufacturer’s wired Ethernet network, just for connecting the manufacturer’s equipment together and if you want to provide the system with an internet connection, to do this by connecting the master MFD wirelessly to our 4GXtream. This will result in having two wired Ethernet networks on the boat, one for the navigation equipment and the other for internet access and normal IT type networking, but it will result in the most reliable operation of the two networks. Most MFD manufacturers do not want customers to open up their Ethernet network to either a conventional LAN or WAN environment that they have no control over. Unknown network devices, levels of network data and protocols, can create interoperability issues that the manufacturer has never tested for, potentially having a serious, negative effect on the operation of their equipment. The MFD’s wireless interface will be on a separate subnet and “locked down” so that it just does what they need it to do and no more. When you tell the wireless interface to join another wireless network in STATION (STA) mode, rather than its default ACCESS POINT (AP) mode, it will get an IP Address for the wireless interface from the 4GXtream and be able to go online for updates, weather data, etc. The following power consumption figures are applicable to both our 4GConnect and 4GConnect Pro models. Power consumption does vary significantly, depending upon the amount of mobile data being transferred and how much wired/wireless network activity is taking place. Below are the average consumption figures for 12v and 24v systems… Minimum – Powered up but no mobile or network data transfer = 1W Normal – Powered up with a couple of network devices doing light internet access = 1.5W Maximum – Powered up with multiple network devices doing heavy internet access = 4.25W In some situations, our 4G Products can appear to be connected to the internet, but due to other external conditions such as AV Software, ISP issues or local network settings, you cannot access websites from your browser. If this happens, there are some additional tests and checks that can be carried out. Go to SYSTEM>ADMINITSTRATION>TROUBLESHOOT and do the following tests…. PING TEST Enter an IP address of 1.1.1.1 and click the PERFORM button. This sends a series of data packets directly to a public website (Cloudflare) which then sends them back to your 4G Product over the Mobile network. The results are shown in the box below and if all of the packets are received, then the connection is good and it might be a DNS issue – continue to the Trace Route Test. Traceroute Test Change the method to Traceroute and the address to www.google.com and click the PERFORM button again, you should see the following info in the box that traces, the route through the internet to the Google web server. If the test fails and the Google site is not reached, then you may have a DNS setting issue on your wireless device. Try setting it to use a fixed DNS server address of 8.8.8.8 which is the Google public DNS server. Check SMS Messages Sometimes, it can be an issue with your mobile network operator account that is stopping the internet access. Please check if you have received any notification SMS messages from the Mobile Operator that might explain why we are connected but not getting a good internet connection? To do this, go to SERVICES>MOBILE UTILITIES>MESSAGES and you should see any SMS messages that the Mobilke operator have sent you… Finally, some anti-virus, VPN or network security software has been known to block mobile internet connections, particularly common on business computers. Try temporarily turning off any anti-virus, VPN or network security software and see if that fixes the problem. If it does, make sure that your new 4G Product is in the list of “Safe Networks” in your anti-virus/security software. Our 4G Products are used globally on lots of different networks and occasionally, due to incorrect APN settings or SIM card issues, a unit will not correctly register on the mobile network and no internet connections will be available. In this situation, please start by checking the SIM card, as per this article that we published on our blog… https://digitalyacht.net/2022/08/12/getting-correct-sim-cards-4g-products/ If that does not resolve the situation, then in order to assist you our support team will need the following screen shots and information… The firmware version is normally displayed in the top right hand section of any of the web pages….example below of the original 4G Connect “Black & White” web interface and the latest “Blue & White” web interface… The 4G Xtream only has a “Blue & White” web interface. Setting up remote access to any network that is operating on a mobile LTE (3G/4G) network is never easy, even for experienced IT engineers. Unfortunately, Digital Yacht just do not have the resources or depth of knowledge to support our customers in doing this on an individual basis. When your remote network is “hidden” inside a mobile network that abstracts all external connections to the internet, the only way to create a VPN is for the 4GConnect/4GXtream to initiate a connection to your VPN server or shared cloud server that does the data routing for you. Our 4GConnect is based on OpenWRT, which supports two different VPN services; OpenVPN and ZeroTier, plus a couple of tunnelling protocols that could be used as an alternative to VPN. If you do not have the services of an experienced IT engineer to help with setting up a solution, then I would look for examples of connecting to a remote OpenWRT network over LTE using VPN services. Here is a link to the OpenVPN documentation on the OpenWRT site and it covers using either a Client or Server setup. Hopefully with this information you will be able to find the relevant settings in our 4G products to setup your VPN. https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/openvpn/start If you have an AT&T Sim Card, then you need to be in “Advanced” Mode, click the word “Basic” in the web page header and then go to Network>Mobile and set the Service Mode to “4G (LTE) Only” and then click the “Save+Apply” button at the bottom of the page…. After the new settings have been applied, go to Network>Interfaces and then click on the “Pencil” Edit button of either MOB1S1A1 (SIM1) or MOB1S2A1 (SIM2) depending upon which SIM slot the AT&T SIM is in…. In the Pop-Up settings window, turn off the Auto APN switch and some new boxes will appear. Select “Custom” from the drop down APN list and then type “Broadband” in the Customer APN box exactly as written with a capital B and then click the “Save+Apply” button at the bottom of the page… After the settings have been applied, go to Status>Overview and check in the Modem panel that you are connected. Now try going to another website to check you have internet. Here is some additional information on the modem LEDs inside the 4GConnect box. The power LED is located on the bottom left corner of the front panel, just under the power connector: It can perform two different actions: The Ethernet port LEDs are located on the router’s front panel, under each respective Ethernet port: They represent activity happening on the router’s Ethernet ports: * The bootloader menu is a special router state from which certain upgrades can be performed. The connection status LEDs are located on the left side of the front panel, between the power connector and the signal strength indication LEDs: he LED displays the router’s current connection state and network type among a few other things: The signal strength LEDs are located in the center of the front panel, to the right of the connection status LEDs: Each lit up LED represents a different value of the router’s current signal strength in RSSI: The signal strength LEDs can also be used as a time indicator for holding the reset button. When you press and hold the reset button, you have to hold it pressed for 5 seconds (by default) to initiate a factory reset. Each second, a new signal strength LED lights up. When all 5 LEDs are lit up, it represents that 5 seconds have passed since you pressed down on the reset button and that you can release it. After releasing the button, all 5 LEDs will start blinking every 1 second. This signifies that the router has begun the factory reset. After the router gets powered up, all signal strength LEDs will turn ON and stay ON for about 40 seconds or until the router’s modem registers on a network – after this, the LEDs will start displaying the router’s current signal strength. If you have a good internet on your 4GConnect, but then the internet connection drops out after a period of time, then this section is for you. Also this is useful for fishermen or blue water sailors who regularly go a long way off shore and then when they return within reception range the 4GConnect does not automatically reconnect. The part below is for the 4G Connect with the black and white interface. First, make sure that “Force LTE Network” and also “Reregister” are both ticked and a time period of 300 secs – as per image below…. If that does not fix things, then please proceed to the Ping Reboot configuration procedure below. Ping Reboot Configuration To enable the “Ping Reboot” feature, go to SERVICES>AUTO REBOOT and you will see a similar page to the one below… I suggest you use the same settings as shown above, which are the ones I have used in all of our testing. Every 5 minutes, it pings 8.8.8.8 which is the Google public DNS server and is always online. If it does not receive a reply within 5 seconds, it retries two more times and if there is still no reply it restarts the 4G Modem. If you have any issue with your 4G product then It is always worth updating your 4G Product to the latest version. This article, although written about the AT&T update, is still applicable for any unit. Updating 4G Firmware Please note that older 4GConnect units must do a two stage update to go from the first “Black and White” web interface version, to the latest “Blue and White” web interface version. The V01.14.05 is a special intermediate version (last of the “Black and White” generation) that must be loaded first, in order to make the jump to the new V07.02.08 firmware. https://digitalyacht.net/2022/03/04/important-update-4g-products/ Configuring 4G Product Here is the link to the very useful video on configuring our 4G Products – shows the latest “Blue and White” web interface… https://digitalyacht.net/2022/03/04/important-update-4g-products/ Getting the correct SIM card Here is the most recent article on SIM cards. If the customer is getting a good mobile phone signal on the 4G Product and the SIM card is being read, the network operator is recognised, etc. then it could be a SIM issue and this article explains what needs to be checked… https://digitalyacht.net/2022/08/12/getting-correct-sim-cards-4g-products/ Manual Reset for 4G Connect To reset one of our 4GConnects, you need to locate the 4GConnect main unit (silver aluminium box with black end caps) and then on the Antenna end cap, there is a small hole to access the reset switch inside – see red square in image below…. NOTE – If you have an older 4GConnect, which did not have the reset hole in the antenna end panel, then go to the next section. With the unit fully powered up (allow 45-60 seconds from turning on the power), use one of those iPhone reset tools or failing that an opened up paper clip, to gently push inside the hole. You will feel a slight resistance and if you continue to gently apply pressure, you should feel the push switch depress (only about 1/32”) and when you do, keep the reset switch depressed for 10-20 secs. When you release it, the 4GConnect should reboot and when it powers back up, all of the settings will be reset to the original ones when it left our factory. The SSID and wireless password will be back to 4GConnect and you should be able to connect wirelessly to it and access the web interface at http://192.168.1.1 where you can sign in with password is 4GConnect again. The only settings I would recommend changing are the APN settings for whatever mobile network SIM you are going to use and then the wireless network name (SSID) and wireless password so that the system is secured so only the owner and friends can connect to it and not anyone who has read the 4GConnect manual and found the default settings. Manual Reset for older 4G Connect To manually reset an older 4GConnect that does not have the reset hole in the antenna end cap, you will need a cross head screwdriver to remove the enclosure end cap that has the three antennas on it. The procedure should be carried out with the 4GConnect powered up, so if you are not doing this on the boat, you will need a 12v 1A DC Power Supply. First unscrew the three antennas (or antenna cables if you have a 4GConnect Pro), by using your fingers on the knurled ring at the base of the antenna… Once the antennas are removed, unscrew the 4x cross head machine screws that hold the end cap on… Gently pull the end cap away from the aluminium enclosure, being careful not to put unnecessary pressure on the three connectors… The reset switch is highlighted in the image above within the red rectangle. Press and hold this switch in for 10-20 secs and when you release it, the 4GConnect should reboot and when it powers back up, all of the settings will be reset to the original ones when it left our factory. The SSID and wireless password will be back to 4GConnect and you should be able to connect wirelessly to it and access the web interface at http://192.168.1.1 where you can sign in with password is 4GConnect again. Since COVID forced many of us to start working remotely, we are seeing an ever increasing demand for our 4G Products. Once installed and working, these products are extremely reliable, but with so many mobile network operators around the world, initial setup can be confusing. To help our customers get up and running as quickly as possible, we have created a new video on configuring our 4G Products. This video is filmed using one of our 4GXtream products, but is equally applicable for our 4GConnect and 4GConnect Pro products, particularly if you have updated to the latest V07.01.02 firmware as detailed in a previous post “Important Update for our 4G Products”. This update adds the same, new “Blue and White” web interface to our 4GConnect, as our 4GXtream has and will be the interface that all future videos and technical documents will be based on. Here’s a quick video showing how to insert a SIM card into the 4G Connect. It also shows how to view the software to check the SIM is registered with the network Our 4GXtream router but also the latest 4G Connect version have a new “Auto-APN” feature that reads the SIM details and selects the correct APN settings for the SIM’s mobile network. APN stands for Access Point Name and are the settings your 4G product needs to pass to the network carrier; AT&T, Vodafone, T-Mobile, etc. in order for the carrier to allocate your 4G product an IP address and connect you to the right secure network. On many networks the new “Auto-APN” feature works very well, but today we had a Vodafone customer contact us who could not get their 4GXtream to connect correctly. The solution was to manually override the APN settings, by following the procedure below. Now go to NETWORK>INTERFACES and click on the Edit button (pencil icon) of the SIM card interface you are using, SIM 1 in the example below. You can now edit the SIM settings to disable Auto-APN mode and add manual “Custom” APN settings, as shown below which are the correct settings for a Vodafone UK (contract) SIM. Once you have set the manual APN settings click the “Save & Apply” button and once the settings have been changed, go to the STATUS>OVERVIEW page to see if you now have a connection to the internet. If your network carrier has not given you your APN settings, then this is a pretty good site to try and we would be really grateful if you could let us know if the Auto-APN settings work for you or what manual settings you had to use. One of the most common problems, that the Digital Yacht support team help our 4G Product customers with, is SIM card issues. This little piece of plastic, with its integrated memory chip, containing a unique identifier, that allows your data usage to be tracked, causes a disproportionate amount of wasted time and effort, so we decided to publish a guide to avoid the pitfalls that we regular see. Not all SIMs are created equal and with the majority aimed at mobile phone users, it is important that the SIM you use in our 4G Products meet the following criteria…. Once you are confident that your SIM meets all of the above criteria, please insert it in to our 4G Product and using the web interface, go to STATUS>NETWORK where you should see a screen similar to the one below, minus the red annotations…. The key pieces of information to look for on this page are that the SIM Card State shows “Inserted”, which means that it has been read by our 4G Product. Then you should see the IMSI and ICCID numbers, which are stored on the SIM and used by the 4G Product to identify itself to the network operator. The IMEI number is unique to the 4G Product’s modem and will always be displayed, even if the SIM is not inserted… Other key information on this page are the Operator and Operator State. The image above was using a SIM from UK operator 3 which was a fully registered, had plenty of Data and had established a data connection. Assuming that you have followed this guide and selected the right SIM card, then there is one last hurdle to overcome, making sure that our 4G Product is using the right APN settings for the SIM’s network operator. The Access Point Name (APN) settings, vary from network operator to network operator, and with the latest firmware updates, our 4G Products will automatically try and set these from a database of popular APN settings. However, for some networks, it is still necessary to manually enter the APN settings, please see our configuration video for more details. Once you have everything working, there should be no need to make any further changes to the settings, but occasionally the connection will fail. This can be for a number of reasons, but more often than not, particularly if you are using a Pay As You Go type SIM or you are using International Roaming, it will be a network operator issue and you should check that you have not received an SMS notification from the operator. To do this, go to the SERVICES>MOBILE UTILITIES>MESSAGES screen where all of the received SMS messages are displayed… Make sure there are no “Data Limit” or “Roaming” related messages that might account for your loss of connectivity and if you are still having problems after rebooting the modem, which you can do at the bottom of the STATUS>NETWORK page, please contact your network operator to check the status of your SIM account. To decide whether to use the Mobile 4G connection or the WL510 long range wireless connection, you will need to go in to the 4GXtream web interface and click on the Network>WAN menu option….which will display the page below. You can use the switches at the end of each line to select whether you want to connect to the internet via Mobile 4G or via the WL510 Wi-Fi on the wired WAN interface. In the screen shot above, taken from my boat’s 4GXtream, I do not have an WL510 wireless booster connected to the Wired WAN interface, so it does not show any information about it but on your unit, with the WL510 connected, there should always be an 192.168.10.xxx IP address and uptime values. Just click Save and Apply after making your selection. If the unit has been working and suddenly stops or you have followed the steps above and everything appears to be OK but you still do not have a connection to the internet, then the fault is likely to be with the SIM or network operator. Could any of the following factors be applicable? The only option in this situation is to contact the network operator, which can be a convoluted exercise, but we have seen this situation many times and if you can get through to the right person and tell them the exact nature of the problem, then it can be resolved. The best source of APN settings is online at https://apnsettings.org and the best way to search for them is to do a Google search like apnsettings.org UK Vodafone 2022 as the search facility on the website is not great. If the default Auto APN setting on the 4GXtream does not work, manually set the APN settings for your SIM card and save them. If they are correct, you should see the Data Connection in the STATUS>OVERVIEW page (see above) shown as Connected and in the NETWORK>WAN page, whichever MOB SIM Slot you are using should have an IP address – in the example below MOB1S2A1 has IP address 10.44.45.58/24 How to configure the LAN port address?
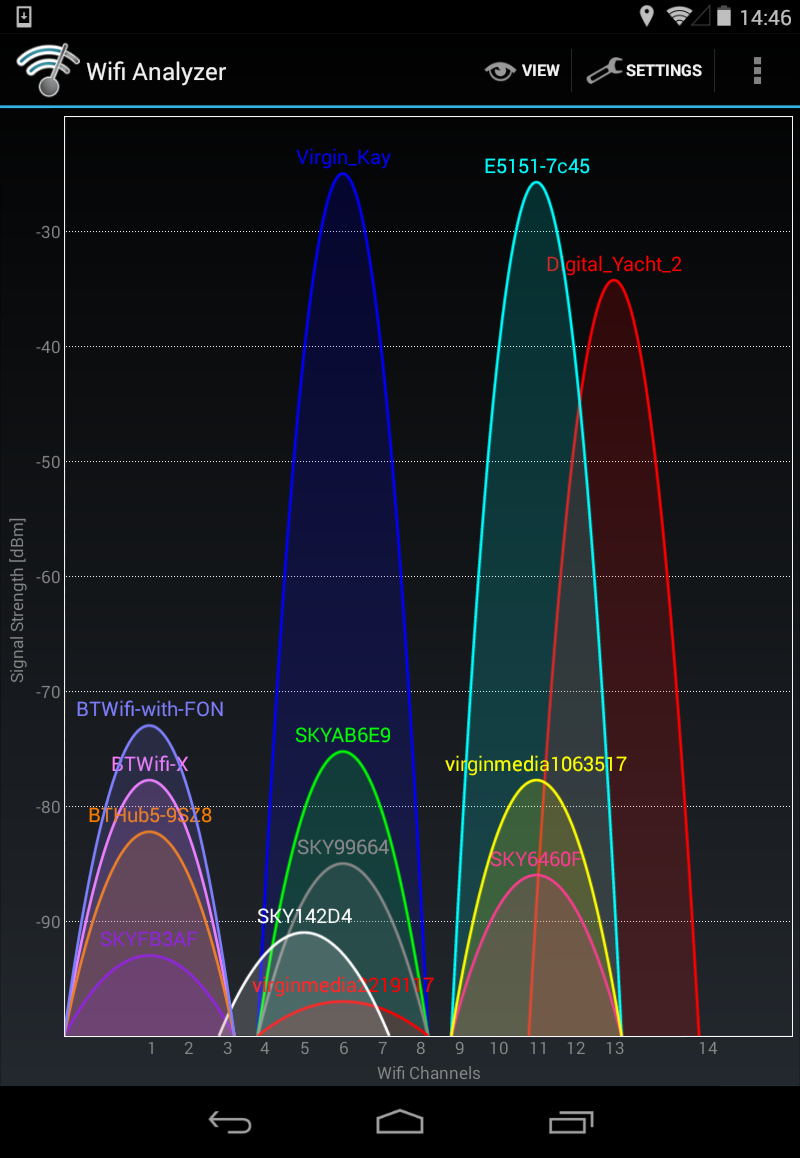
Slow internet speed through WiFi on my 4G Router
Boat remote access thought 4G – Port Forwarding to remote view CCTV system
Manual APN Settings for latest EE SIM cards
Connecting other Marine Electronic Equipment to our 4G Products
4GConnect Power Consumption
Advanced Diagnostic Tests for our 4G/5G Products
Generating Diagnostic Information on our 4G/5G Products
How to tell what firmware your 4GConnect or 4GXtream has?
VPN on our 4G Products
I want to set up my AT&T Sim card
4GConnect Status LEDs Information
Power LED

ACTION
DESCRIPTION
LED turned ON
Router is powered up
LED turned OFF
Router is not powered up
Ethernet port LEDs

ACTION
DESCRIPTION
LED turned ON
Operating as a 10/100 Mbps connection
LED turned OFF
No link established
LED blinking
Connection established and there is activity on this port (data being transferred)
LEDs light up and turn OFF in sequence from WAN port to LAN1 port
The router is in the bootloader menu state*
Connection status LEDs

ACTION
DESCRIPTION
2G, 3G and 4G LEDs blinking every 1 second
No SIM or bad PIN
Blinking from 2G LED to 4G LED repeatedly
SIM holder is not inserted or access to network is denied
2G/3G/4G LED blinking every 1 sec
Connected to 2G/3G/4G, no data session established
2G/3G/4G LED turned on
Connected to 2G/3G/4G with data session
2G/3G/4G LED blinking rapidly
Connected to 2G/3G/4G with data session and data is being transferred
Signal strength LEDs

NO. OF LIT UP LEDs
SIGNAL STRENGTH VALUE
0
≤ -111 dBm
1
-110 dBm to -97 dBm
2
-96 dBm to -82 dBm
3
-81 dBm to -67 dBm
4
-66 dBm to -52 dBm
5
≥ -51 dBm
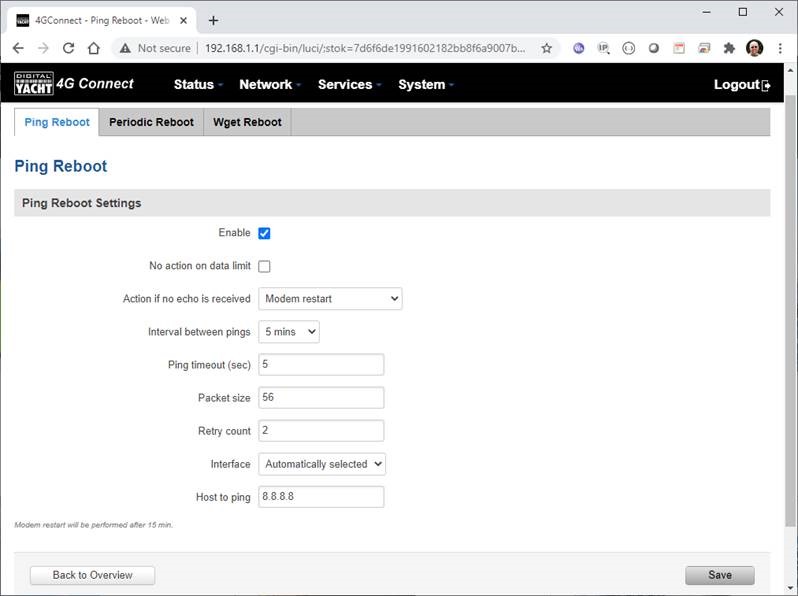
4GConnect Mobile Network Disconnection
General Information on 4G/5G Products (Configuration, updates, SIM cards)
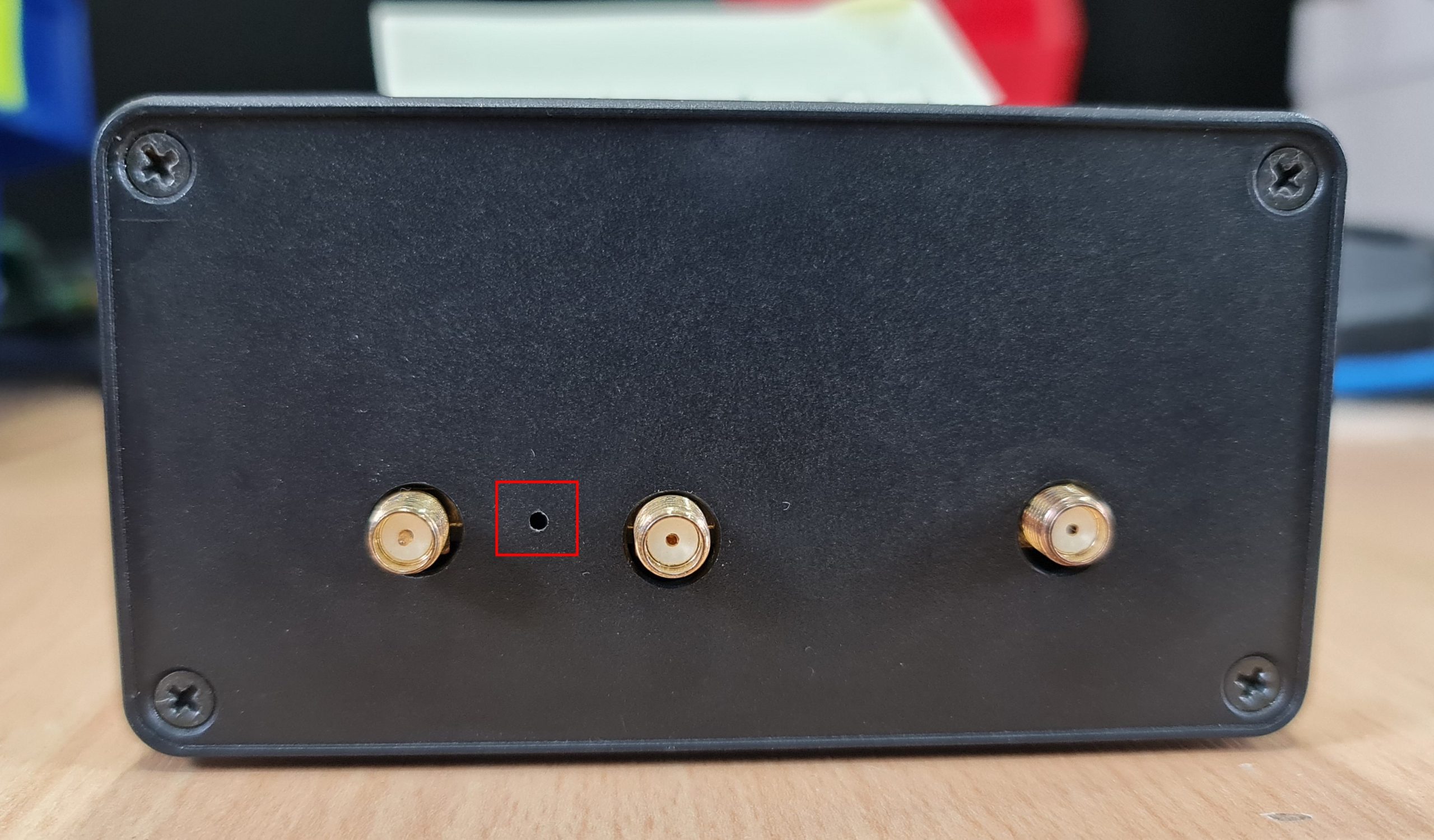
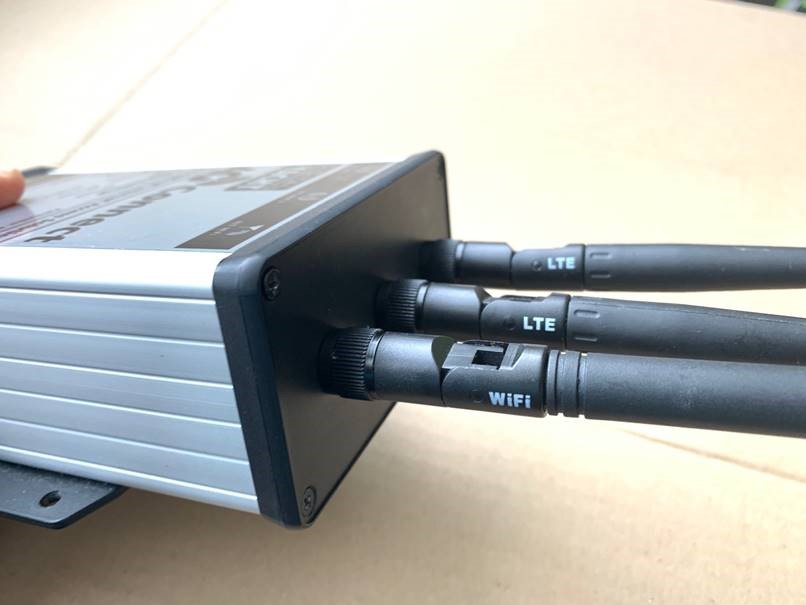
How to manually reset the 4GConnect?



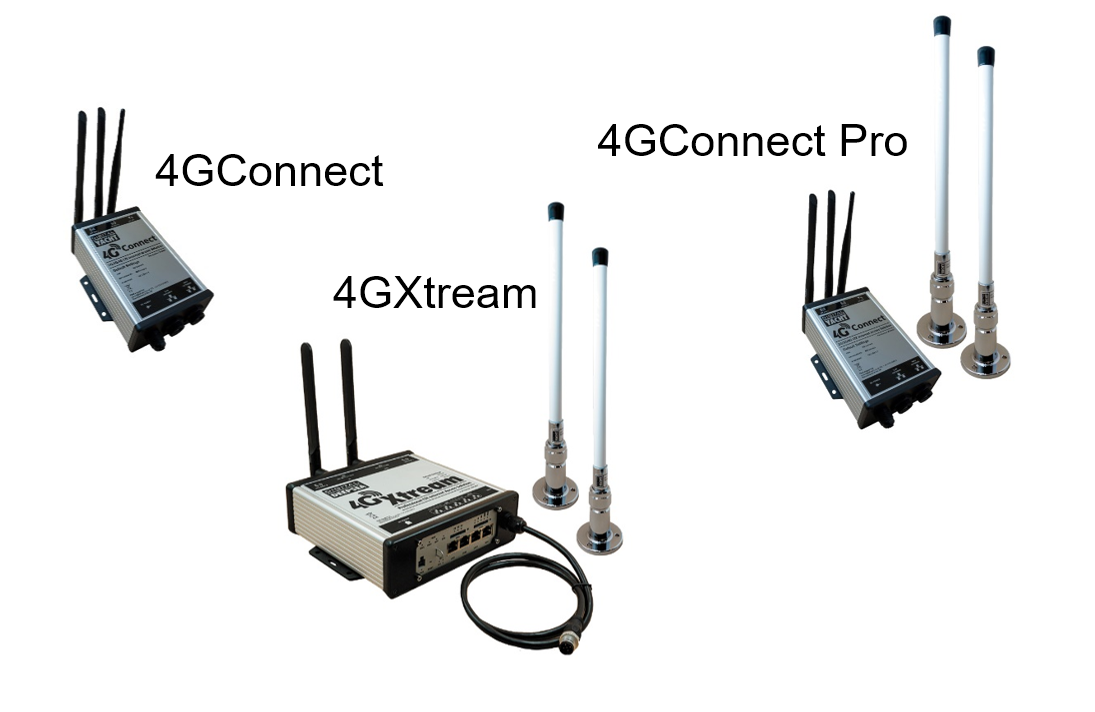
How to configure our 4G products?

How to insert a SIM card into 4G Connect?
How to override the Auto-APN Settings?
Getting the Correct SIM cards for our 4G Products
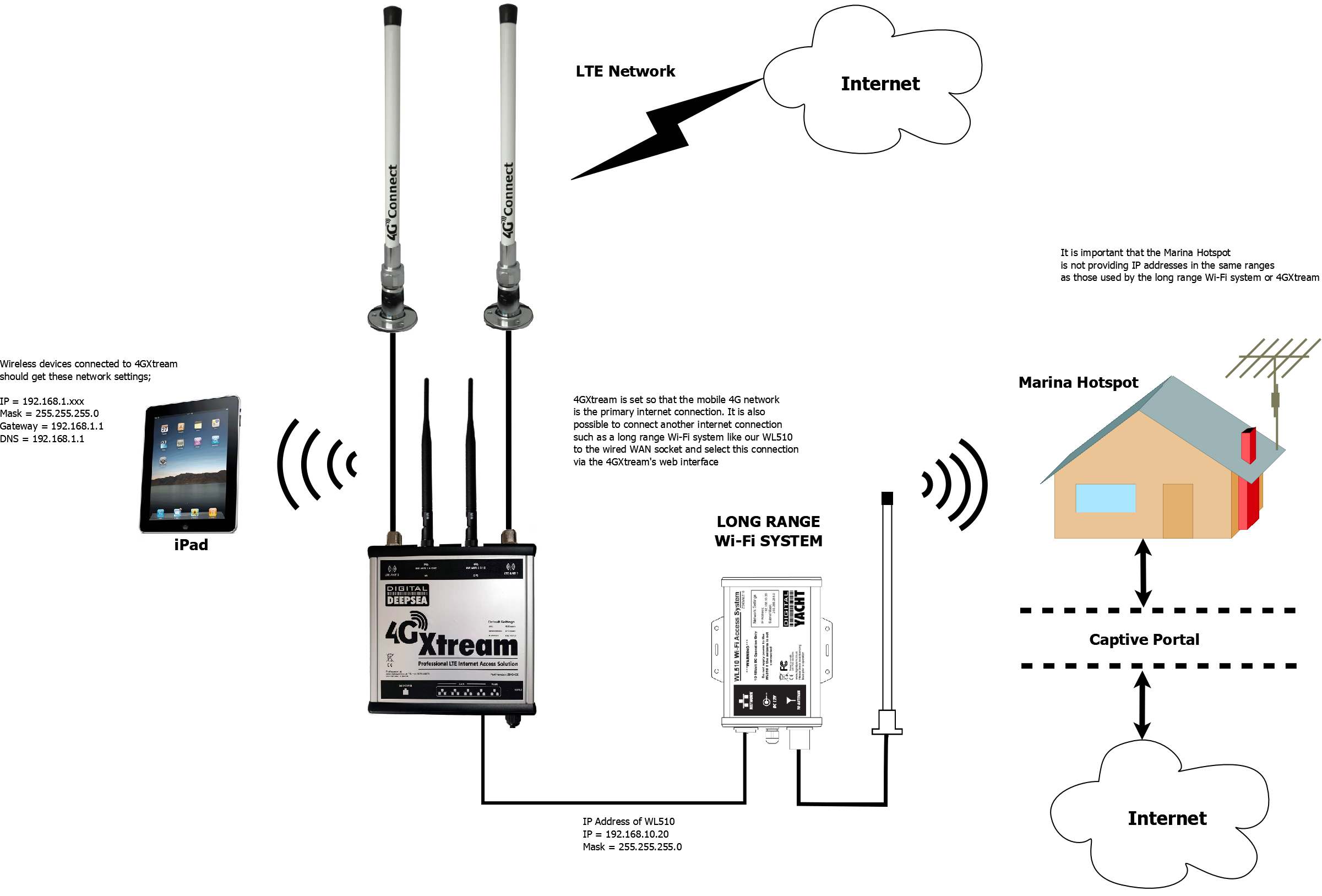
Using WL510 with 4GXtream
Is the SIM or Network Operator causing the problem?
Are the APN Settings Correct?